Waste management is an important aspect of modern society, and one of the methods used to reduce the volume of waste is incineration. Incinerators are designed to burn waste materials at high temperatures, reducing them to ash and other by-products. However, there are different types of incinerators, each with its own set of pros and cons. Here, we take a closer look at the different types of incinerators and discuss which might be the best option for your waste management needs.
1. Grate-based incinerators:
Grate-based incinerators are the most common type of incinerators used for municipal solid waste. They use a moving grate to feed waste into the combustion chamber, where it is burned at high temperatures. One of the main advantages of grate-based incinerators is that they can handle a wide variety of waste materials, including bulky items and mixed materials. However, they require a constant supply of waste to maintain high temperatures, which can be a challenge for smaller facilities with inconsistent waste streams.
2. Rotary kiln incinerators:
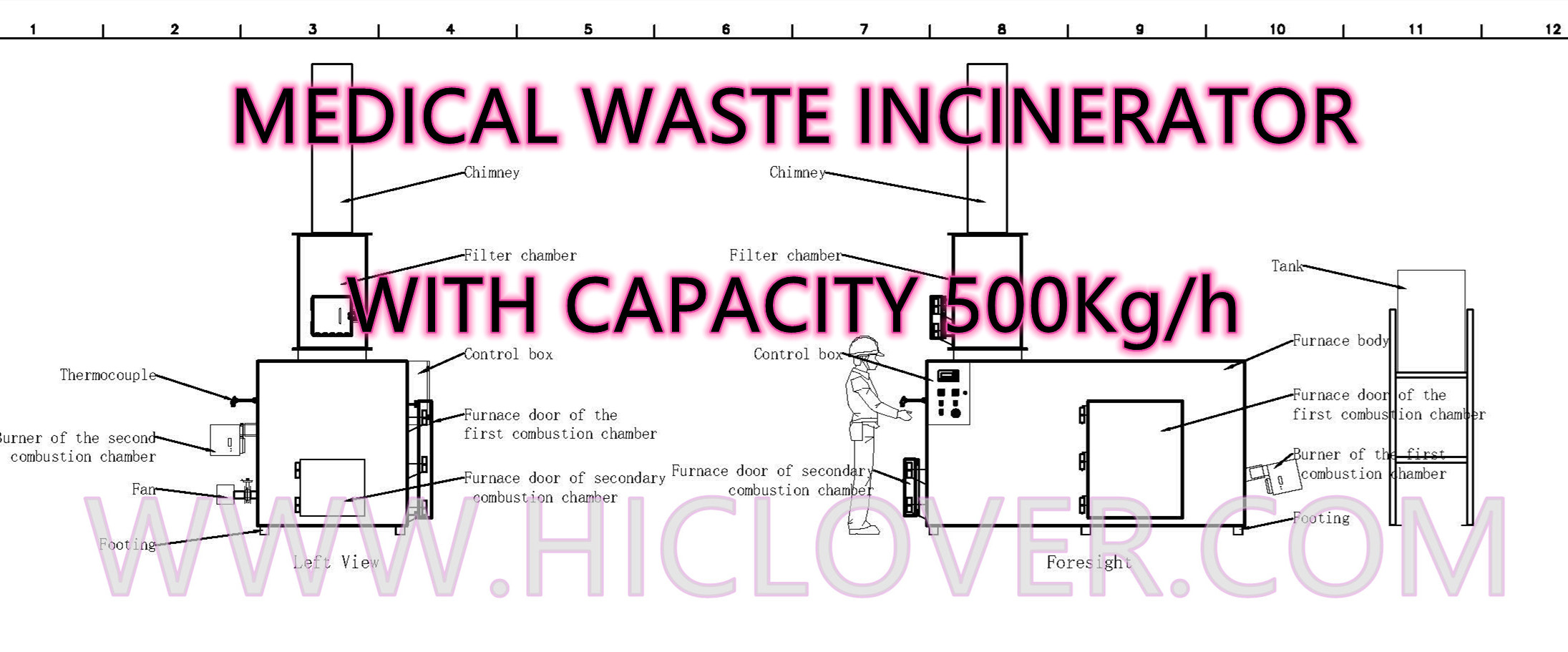
Rotary kiln incinerators are used for the disposal of hazardous waste and medical waste. These incinerators use a rotating chamber to ensure even distribution of heat, which is essential for the complete combustion of hazardous materials. One of the main advantages of rotary kiln incinerators is their high operating temperatures, which can effectively destroy harmful substances. However, they require a constant supply of fuel to maintain the high temperatures, and they can be costly to operate.
3. Fluidized bed incinerators:
Fluidized bed incinerators use a bed of inert material (such as sand) to support the waste materials and maintain a high temperature. This type of incinerator is ideal for the incineration of high-moisture waste materials, as the fluidized bed helps to evaporate the moisture and reduce the risk of incomplete combustion. However, fluidized bed incinerators require a complex system to control air flow and temperature, and they can be expensive to install and operate.
4. Gasification incinerators:
Gasification incinerators use high temperatures and limited oxygen to convert waste materials into a synthetic gas, which can be used as a fuel source. This type of incinerator is ideal for the disposal of organic waste, as it can effectively convert it into a useful energy source. However, gasification incinerators require a complex system to control the gasification process, and they can be costly to operate.
In conclusion, each type of incinerator has its own set of pros and cons, and the best option for your waste management needs will depend on the type and volume of waste you need to dispose of. Grate-based incinerators are best suited for municipal solid waste, while rotary kiln incinerators are ideal for hazardous and medical waste. Fluidized bed incinerators are well-suited for high-moisture waste materials, and gasification incinerators are ideal for organic waste. It is important to carefully consider the specific needs of your facility before choosing an incinerator for waste management.