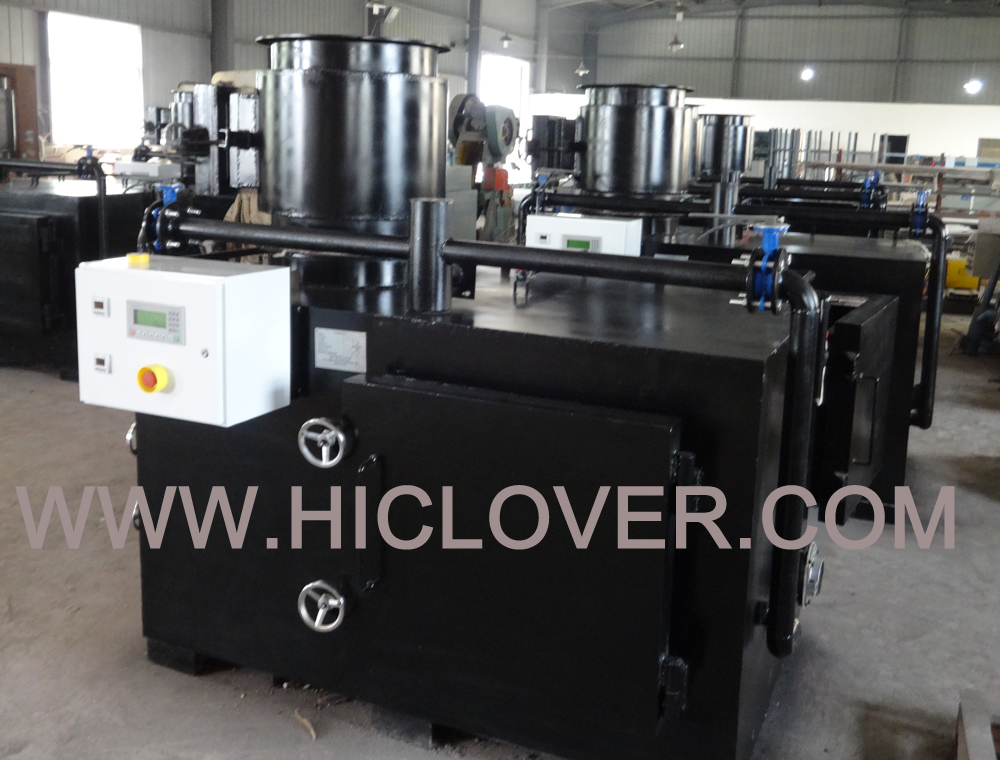
Incineration is a process of waste treatment that involves the combustion of organic substances contained in waste materials. It is a critical waste management method that helps in reducing the volume of waste and makes it easier to handle and dispose of the residues. Understanding the incineration process is essential for ensuring that it is carried out effectively and efficiently. To help in this, a step-by-step flow diagram of the incineration process will be outlined in this article.
Step 1: Waste Reception – The first step in the incineration process is the reception of the waste materials. The waste is brought to the incineration facility and undergoes a thorough inspection to ensure that it meets the requirements for incineration. Hazardous or non-compliant waste is separated and managed appropriately.
Step 2: Waste Storage – The waste materials are then stored in a designated area within the facility. Proper storage is essential to ensure the efficient feeding of waste into the incinerator and to maintain an organized and safe working environment.
Step 3: Waste Feeding – The waste materials are fed into the incinerator using a conveyor system or other automated feeding mechanisms. The feeding process must be carefully controlled to ensure a consistent and optimal flow of waste into the incinerator.
Step 4: Combustion Chamber – Once inside the incinerator, the waste materials are subjected to high temperatures in the combustion chamber. The organic substances in the waste are burned, resulting in the release of heat energy that can be harnessed for various purposes, such as electricity generation or steam production.
Step 5: Air Pollution Control – The combustion process produces emissions that need to be carefully managed to minimize their environmental impact. Air pollution control systems, such as scrubbers, electrostatic precipitators, and baghouses, are used to remove pollutants from the combustion gases before they are released into the atmosphere.
Step 6: Heat Recovery – As mentioned earlier, the combustion process generates heat energy that can be recovered and utilized. Heat exchangers are employed to capture the heat from the combustion gases, which can then be used to produce steam for electricity generation or other industrial processes.
Step 7: Residue Treatment – After the combustion process, the remaining residues, such as ash and other solid materials, are collected and treated. Depending on the nature of the residues, they may be recycled, reused, or disposed of in an environmentally responsible manner.
Step 8: Emission Monitoring – Throughout the incineration process, emissions of pollutants are continuously monitored to ensure compliance with regulatory standards and to uphold environmental and public health and safety.
By understanding the step-by-step flow diagram of the incineration process, waste management professionals and stakeholders can gain insights into the operational and environmental considerations of incineration. This understanding is crucial for ensuring that incineration is carried out in a safe, efficient, and environmentally responsible manner. It also underscores the significance of proper waste segregation, treatment, and disposal to maximize the benefits of incineration while minimizing its potential negative impacts.