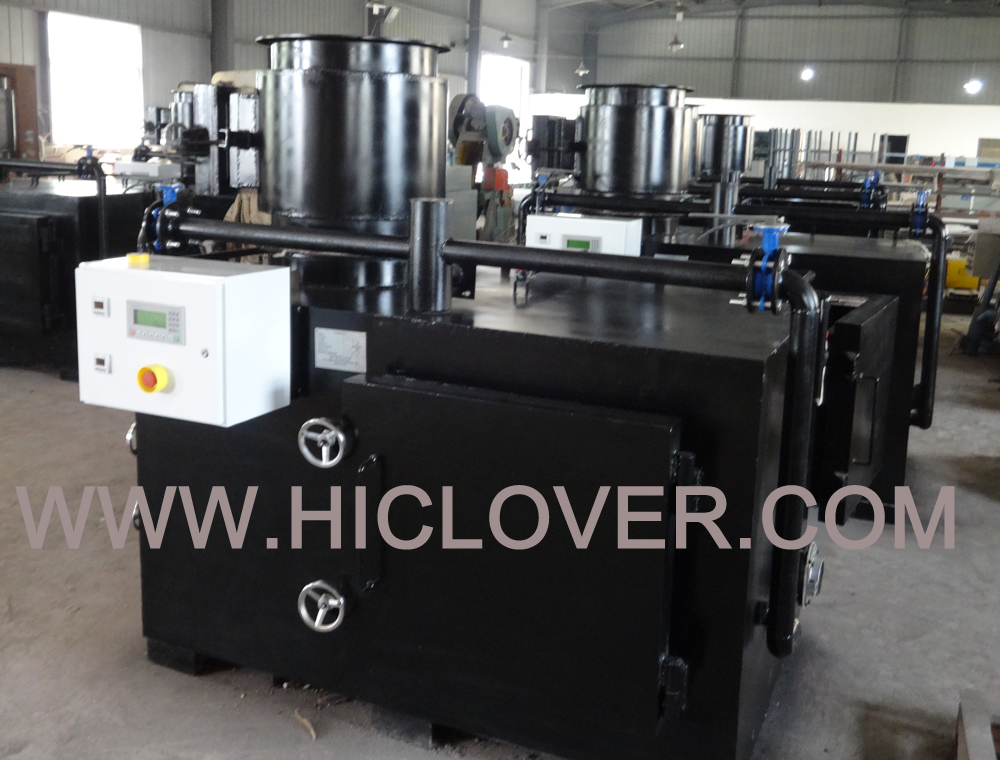
Incinerators have become an increasingly popular method for disposing of waste in recent years. As concerns about environmental sustainability and the effects of waste on the planet continue to grow, more and more countries are turning to incineration as a way to manage their waste in a cost-effective and environmentally friendly manner. However, as incinerators become more prevalent, understanding the economics behind them is becoming increasingly important for businesses and policymakers alike.
One of the key factors in understanding the economics of incinerators is the price of waste disposal. The cost of incineration can vary depending on a number of factors, including the type of waste being incinerated, the location of the incinerator, and the technology used in the incineration process. In general, however, incineration tends to be a relatively cost-effective method of waste disposal when compared to other options such as landfilling or recycling. This is because incineration not only reduces the volume of waste that needs to be disposed of, but it also produces energy in the form of heat and electricity. This can help to offset the costs of operating the incinerator, making it a more attractive option for waste management.
Another important factor in understanding the economics of incinerators is market trends. As incineration becomes more widespread, the market for waste disposal is becoming increasingly competitive. This has led to a number of new developments in the industry, including the development of more efficient and environmentally friendly incineration technologies, as well as the implementation of stricter regulations and standards for waste management. These market trends are shaping the way that incinerators are operated and the prices that are charged for waste disposal, making it essential for businesses and policymakers to stay abreast of these developments in order to make informed decisions about waste management.
In addition to market trends, the economics of incinerators are also influenced by government policies and incentives. Many countries offer subsidies and tax breaks for businesses that invest in incineration technology, in an effort to encourage the adoption of more sustainable waste management practices. These incentives can significantly impact the economics of incineration, making it a more financially viable option for businesses looking to dispose of their waste in a responsible and cost-effective manner.
Ultimately, the economics of incinerators are complex and multifaceted, influenced by a wide range of factors including market trends, government policies, and technological advancements. By understanding these factors and staying abreast of developments in the industry, businesses and policymakers can make informed decisions about their waste management practices, ensuring that they are not only economically viable but also environmentally sustainable. With the right knowledge and understanding, incinerators can play a crucial role in addressing the growing problem of waste management in a way that is both economically and environmentally responsible.