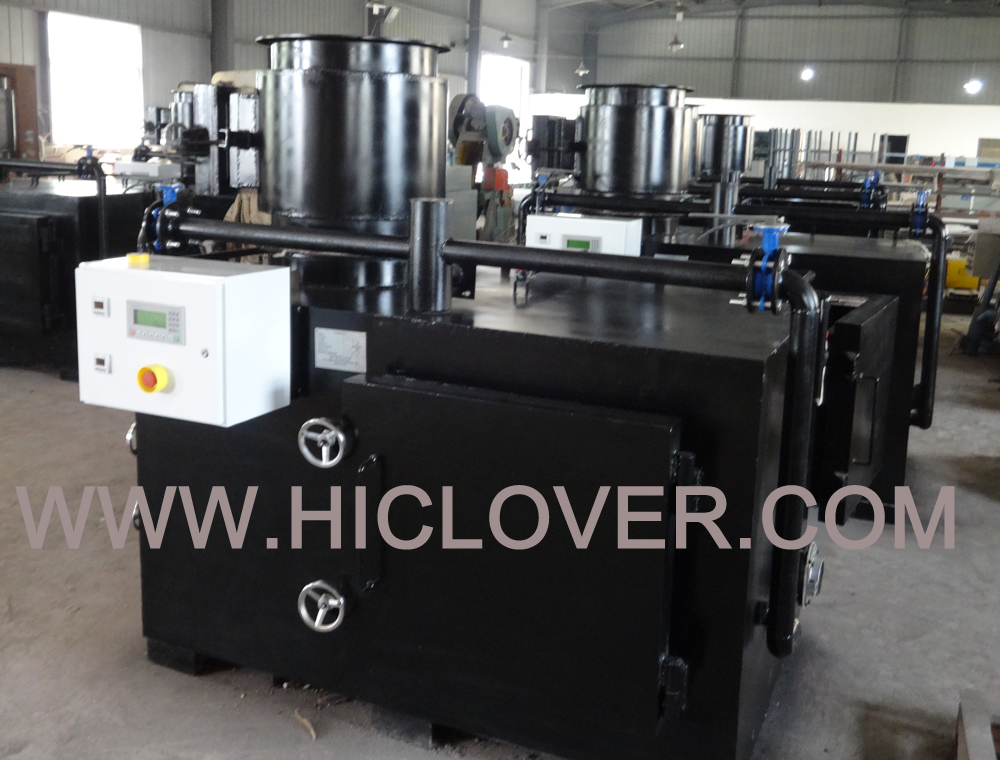
Medical waste incineration is a common method for disposing of medical waste such as contaminated sharps, pathological waste, and other hazardous materials produced by healthcare facilities. While incineration is often seen as an efficient and cost-effective way to eliminate these potentially dangerous materials, the process has several significant consequences that are often overlooked.
One of the most concerning consequences of medical waste incineration is the release of harmful pollutants into the atmosphere. When medical waste is burned, it releases a variety of toxic substances, including dioxins, furans, mercury, and other heavy metals. These pollutants can have serious health implications for both humans and the environment. Exposure to dioxins and furans has been linked to an increased risk of cancer, reproductive and developmental disorders, immune system suppression, and other health problems. Additionally, mercury and other heavy metals can accumulate in the food chain, posing a risk to wildlife and human health.
In addition to air pollution, medical waste incineration also produces ash residue that can contain high levels of toxic contaminants. This ash must be carefully disposed of to prevent it from leaching into the surrounding environment and contaminating water sources. Improper handling of incinerator ash can lead to groundwater and soil contamination, further impacting the health of surrounding communities and ecosystems.
Furthermore, the impact of medical waste incineration extends beyond environmental and human health concerns. The process also consumes significant amounts of energy and contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. While some modern medical waste incinerators are designed to capture and treat emissions, many facilities in developing countries and underserved communities do not have the infrastructure or resources to implement these technologies, leading to uncontrolled and harmful releases of pollutants.
It is important to consider alternative methods for the disposal of medical waste that are less harmful to the environment and human health. One such method is autoclaving, which uses steam and high pressure to sterilize medical waste before it is sent to a landfill. Other options include chemical treatment, microwaving, and non-incineration waste-to-energy technologies that can convert medical waste into electricity or heat without the release of harmful pollutants.
In conclusion, the consequences of medical waste incineration are far-reaching and often overlooked. As healthcare facilities continue to generate large quantities of medical waste, it is essential to prioritize the adoption of sustainable and environmentally friendly waste disposal methods. By taking proactive steps to reduce and properly manage medical waste, we can protect the health of both people and the planet.